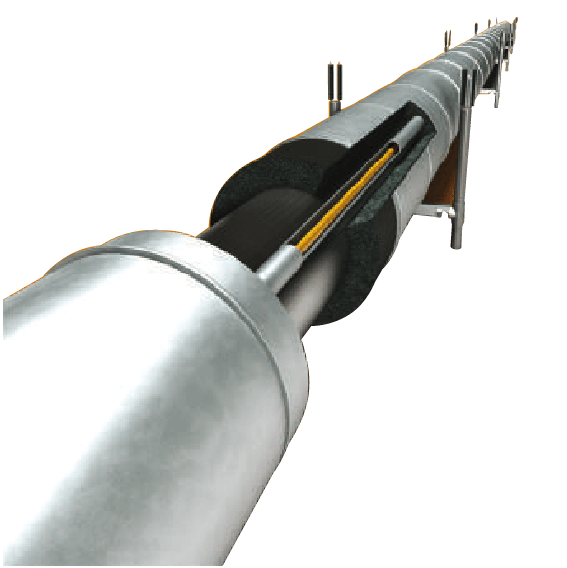
Heating Cable

Heating cables, also known as heat trace cables or heater cables, are essential components in various heating systems. They are designed to maintain or raise the temperature of pipes, tanks, roofs, and other surfaces. By converting electrical energy into heat, these cables prevent freezing, ensure smooth operation in industrial processes, and protect against the build-up of ice in gutters and roofs. The flexibility and efficiency of heating cables make them suitable for both residential and commercial applications, where precise temperature control is necessary. Their versatility and reliability have made them a popular choice across various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and food and beverage manufacturing.

What is a Heating Cable?
A heating cable, often referred to as a heat cable or heated cable, is an electrical device designed to produce heat. These cables are constructed with conductive materials that generate heat when electricity passes through them. The primary function of a heating cable is to prevent the freezing of pipes, roofs, and gutters, or to maintain the desired temperature of various surfaces and systems.
Heating cables come in different types, such as self-regulating cables that adjust their heat output based on the surrounding temperature and constant wattage cables that provide a steady amount of heat. This makes them versatile for a range of applications, from residential use in preventing frozen pipes to industrial settings where maintaining process temperatures is crucial. Their design ensures durability and efficiency, making them a reliable choice for long-term heating solutions.
What is the Purpose of Heating Cable?
The primary purpose of a heating cable is to provide consistent and reliable heat to prevent damage and ensure the proper functioning of systems and surfaces exposed to cold temperatures. In residential settings, heating cables are commonly used to prevent water pipes from freezing, which can lead to costly repairs and water damage. In commercial and industrial environments, they are essential for maintaining the necessary temperatures of pipes and equipment, preventing process disruptions due to cold weather.
Additionally, heating cables are utilized to eliminate the build-up of ice on roofs and in gutters. This helps to prevent ice dams that can cause structural damage to buildings and pose safety hazards. In industrial applications, these cables are vital for maintaining fluid flow in pipelines and tanks, ensuring that processes are not hindered by the effects of freezing temperatures. Thus, heating cables serve as an effective solution for temperature maintenance, safety, and protection across various applications.
Where is the Heating Cable Used?
Heating cables are utilized in a wide range of applications across residential, commercial, and industrial settings. In residential homes, these cables are primarily used to prevent pipes from freezing during the winter months. They can be installed on pipes that are exposed to cold environments, such as basements, crawl spaces, or external walls, ensuring the water inside remains at a temperature above freezing. Additionally, heating cables are commonly used on roofs and in gutters to prevent the formation of ice dams, which can cause significant damage to the structure and roofing materials.
In industrial and commercial settings, heating cables play a crucial role in maintaining process temperatures in pipelines, tanks, and vessels. They are essential in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals, where maintaining a specific temperature is critical for product quality and operational efficiency. Heating cables are also employed in freeze protection for fire protection systems, sprinkler systems, and in-ground heating for outdoor spaces like driveways and sidewalks to prevent ice formation.
Pipe Heating Cable
A pipe heating cable, also known as a pipe heat cable or water pipe heating cable, is specifically designed to prevent pipes from freezing in cold weather. These cables are wrapped around or run alongside pipes and emit heat to keep the water inside at a temperature that prevents freezing. They are especially useful for pipes that are exposed to freezing temperatures, such as those in unheated basements, crawl spaces, or outside areas.
Pipe heating cables come in different types, including self-regulating cables that adjust their heat output depending on the ambient temperature and constant wattage cables that provide a steady level of heat. This flexibility allows for effective freeze protection for a variety of pipe materials, including metal and plastic. By using pipe heating cables, homeowners and businesses can avoid the costly repairs associated with burst pipes and ensure a continuous water supply throughout the winter.
Roof Heating Cable
Roof heating cables, often referred to as roof heat cables or heated cables for roofs, are installed to prevent ice dams and the build-up of snow on rooftops. These cables are strategically placed along the roof edges and in valleys where snow and ice typically accumulate. When activated, the cables melt snow and ice, allowing water to drain safely into the gutters and downspouts.
This type of heating solution is especially useful in regions that experience heavy snowfall and cold temperatures, which can lead to significant ice accumulation on roofs. By preventing the formation of ice dams, roof heating cables protect the structural integrity of the roof, reduce the risk of leaks and water damage, and enhance overall building safety. They are a cost-effective measure for prolonging the lifespan of roofing materials and ensuring proper drainage during the winter months.
Heating Cable for Gutters
Heating cables for gutters, also known as gutter heating cables or gutter heater cables, are specifically designed to prevent ice build-up in gutters and downspouts. These cables are installed inside gutters and along the edges of roofs to maintain a clear path for melting snow and ice, preventing blockages that can lead to water overflow and damage to the building’s structure.
The primary benefit of using heating cables in gutters is to prevent ice dams and icicles that can cause significant damage to the gutter system and pose a risk to pedestrians below. By ensuring a continuous flow of melted water, these cables protect against potential leaks, gutter detachments, and structural damage, making them an essential tool for property maintenance in cold climates.
Tank Heating Cable
Tank heating cables are designed to maintain or increase the temperature of liquids stored in tanks, ensuring that they remain at the desired temperature even in cold environments. These cables are commonly used in industrial settings where temperature control is crucial, such as in the storage of chemicals, fuels, oils, or food products. By wrapping the cables around the exterior of the tank, they provide consistent heat, preventing the contents from freezing or becoming too viscous to pump or process effectively.
The use of tank heating cables is vital in industries such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, where maintaining a stable temperature is essential for safety, compliance, and efficiency. These cables can be customized to fit tanks of various sizes and shapes, and are designed to operate efficiently in harsh conditions, ensuring reliable performance over time.
How Does a Heating Cable Work?
A heating cable works by converting electrical energy into heat. The cable is composed of a conductive core, typically made of materials like copper or nickel-chrome, which generates heat when an electric current passes through it. The cable is insulated to protect against moisture and mechanical damage, and an outer jacket is added to provide additional durability and safety.
There are two primary cable types of heat trace: self-regulating and constant wattage. Self-regulating heating cables adjust their heat output based on the surrounding temperature; as the temperature drops, the cable increases its heat output, and as the temperature rises, it reduces its heat output, making it energy-efficient and ideal for freeze protection. Constant wattage cables, on the other hand, deliver a consistent level of heat regardless of the surrounding conditions, making them suitable for applications requiring uniform heat. These cables are controlled by thermostats or sensors to maintain the desired temperature, ensuring efficiency and safety in various applications.
 Türkçe
Türkçe