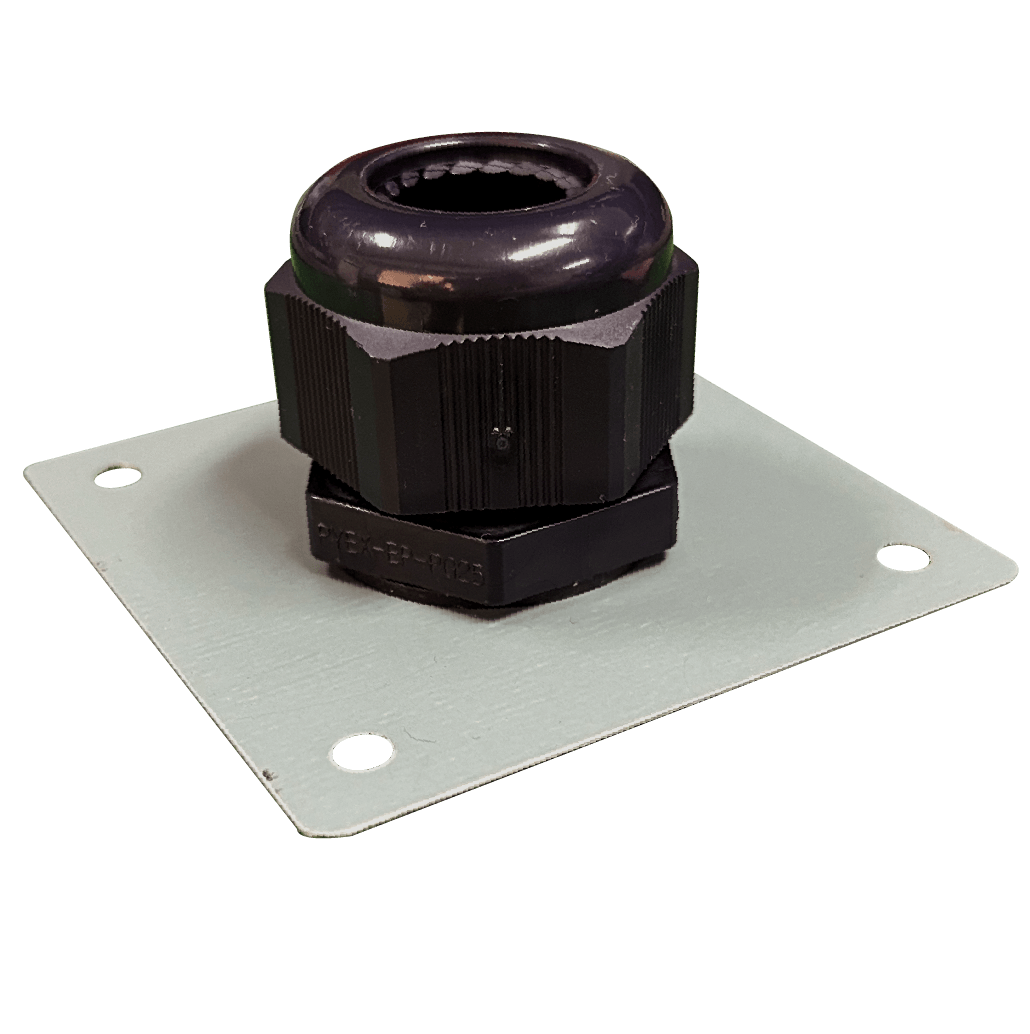
PYEX-IE-PG25

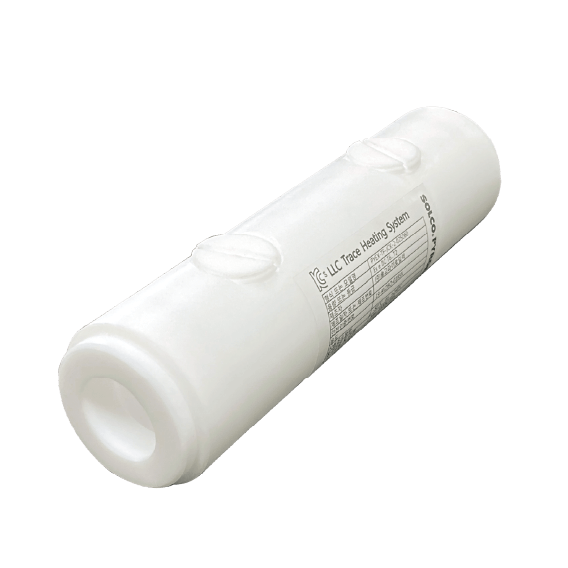
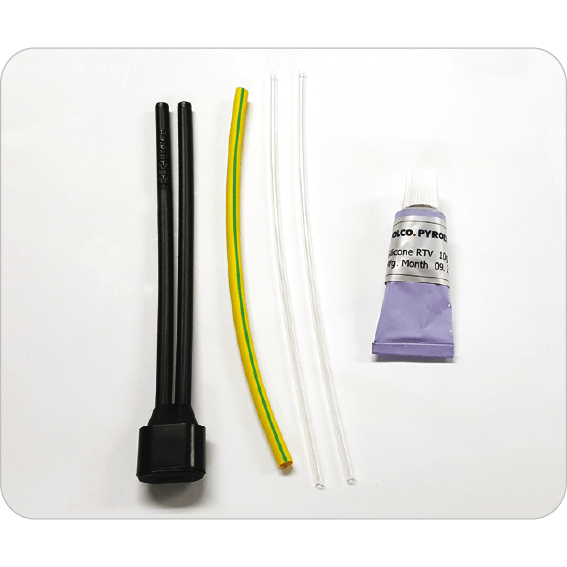
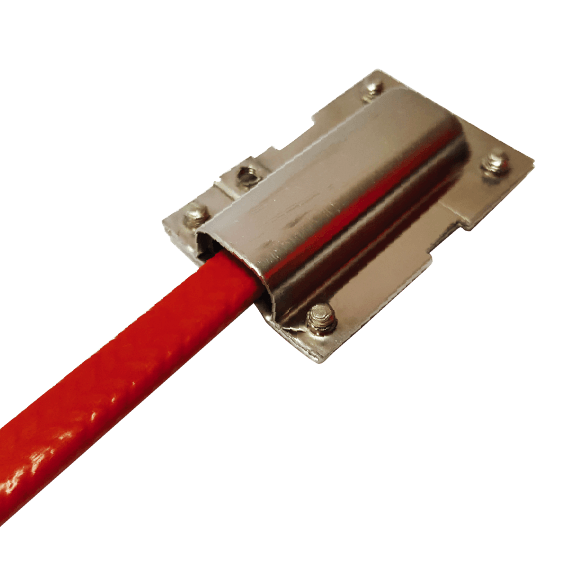
PYEX-IE-PG25 Cladding Mounted Insulation Entry Kit
SOLCO PYROELEC cladding mounted insulation entry kits for the protection of power and heat trace cables when passing through thermal insulation cladding on pipes, tanks, or vessels.
Cable Gland PYEX-IE-PG25
A cable gland is an essential component used in electrical and industrial applications to secure and protect cables as they pass through enclosures. It ensures a firm grip on the cable while providing environmental protection against dust, moisture, and mechanical stress. These glands come in various materials and designs, catering to different industries such as construction, marine, and hazardous environments. Choosing the right sealed cable gland is crucial for maintaining electrical integrity and safety in any installation.
What is a Cable Gland?
A cable gland is a mechanical device designed to secure electrical cables and provide protection against environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and mechanical strain. It acts as a sealing and terminating component, ensuring that cables remain securely in place while preventing damage caused by movement or external elements.
Cable glands are commonly used in electrical installations, industrial machinery, telecommunications, and hazardous environments. They come in different materials such as brass, stainless steel, and polyamide, each offering unique advantages depending on the application. The cable gland dimensions and cable gland diameters must be carefully selected to match the cable size and ensure a tight fit.
One of the key benefits of using a sealed cable gland is its ability to maintain an enclosure's ingress protection (IP) rating. This is essential in industries like oil and gas, where exposure to water, dust, and chemicals can compromise electrical systems. Properly installed electrical cable glands enhance safety, reduce the risk of short circuits, and prolong the life of the equipment.
What Does a Cable Gland Do?
A cable gland performs multiple crucial functions in electrical and industrial applications. Its primary role is to secure and protect electrical cables as they pass through panels, enclosures, or equipment housings. By providing a firm grip, the gland prevents cable movement, reducing the risk of mechanical stress and potential damage.
Another key function of a sealed cable gland is to offer environmental protection. It helps maintain an enclosure’s integrity by preventing the entry of dust, water, and other contaminants. This is particularly important in outdoor and industrial settings where harsh conditions can degrade cable insulation and lead to system failures.
Additionally, cable glands ensure electrical safety by grounding and bonding cables. Certain types, such as metal cable glands, provide electromagnetic shielding, which is essential in sensitive electronic applications. In hazardous locations, ex-proof cable glands are used to prevent sparks and explosions, ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Types of Cable Glands
Cable glands come in various types, designed to meet specific industrial and environmental requirements. The selection of a cable gland depends on factors such as material, sealing capability, and the intended application. Below are some of the most common types:
Metal Cable Gland
A metal cable gland is made from durable materials such as brass, aluminum, or stainless steel. These glands are known for their high strength, resistance to corrosion, and ability to provide electromagnetic shielding. They are commonly used in industrial, marine, and hazardous environments where durability and safety are essential.
Polyamide Cable Gland
A polyamide cable gland is made from high-quality plastic, offering excellent resistance to chemicals and UV radiation. These glands are lightweight and cost-effective, making them suitable for indoor applications, telecommunications, and non-corrosive environments. They provide reliable sealing while ensuring flexibility in cable management.
Uses of Cable Glands
Cable glands are used in a wide range of industries and applications to ensure the safety and longevity of electrical installations. They provide mechanical support, environmental protection, and secure cable entry points in various settings. Below are some key uses of electrical cable glands:
- Industrial Applications: Used in factories, power plants, and processing facilities to protect cables from dust, moisture, and mechanical stress.
- Marine and Offshore Installations: Stainless cable glands are preferred in these environments due to their resistance to saltwater corrosion.
- Hazardous Areas: In explosive atmospheres such as oil refineries and chemical plants, ex-proof cable glands prevent sparks and ignition risks.
- Telecommunications: Protects fiber optic and data cables from external interference and mechanical damage.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Used in solar panels and wind turbines to ensure long-term durability and weather resistance.
Ex-Proof Cable Glands for Explosive Environments
An ex-proof cable gland is specifically designed for use in hazardous areas where explosive gases or dust particles are present. These glands prevent sparks from escaping the enclosure, ensuring compliance with safety standards such as ATEX and IECEx. Industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and mining rely on ex-proof glands to prevent fire hazards and explosions.
Cable Gland Prices
The cost of a cable gland varies depending on several factors, including material, size, certification, and application requirements. Here are some key factors that influence cable gland prices:
- Material: Metal cable glands (such as brass or stainless steel) tend to be more expensive than polyamide cable glands due to their durability and resistance to harsh environments.
- Size and Specifications: Larger cable gland dimensions and special sealing features increase the cost.
- Certifications: Ex-proof cable glands and those with high IP ratings (e.g., IP68) are priced higher due to their specialized design for hazardous environments.
- Brand and Manufacturer: Well-known brands often charge a premium for their high-quality products, warranties, and industry approvals.
- Quantity and Bulk Purchases: Buying cable glands in bulk can reduce the per-unit cost, making it more cost-effective for large-scale projects.
For those requiring long-lasting and corrosion-resistant options, stainless cable glands are a reliable but slightly more expensive choice. Meanwhile, detachable cable glands may offer flexibility but could also impact the pricing depending on their design and ease of installation.
Considerations in Cable Gland Selection
Choosing the right cable gland is crucial for ensuring safety, durability, and compatibility with the intended application. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Cable Gland Dimensions & Diameters: The gland must match the cable size to ensure a secure and sealed connection. Incorrect sizing can lead to mechanical strain or leakage.
- Material Selection: Metal cable glands (such as brass or stainless steel) are ideal for industrial and outdoor applications, while polyamide cable glands are suitable for indoor and less demanding environments.
- Sealing & Protection: A sealed cable gland with high IP ratings (IP67, IP68) ensures protection against water and dust, which is critical for outdoor and hazardous areas.
- Application Environment: Ex-proof cable glands are required in explosive atmospheres, whereas stainless cable glands are best for corrosive environments like marine and chemical industries.
- Installation & Maintenance: Some applications benefit from detachable cable glands, allowing easy removal and reinstallation without damaging the cable or enclosure.
- Compliance & Certification: Ensure the gland meets industry standards such as ATEX, IECEx, or UL, depending on the specific application requirements.
Maintenance and Life Extension Methods of Cable Glands
Proper maintenance of cable glands is essential to ensure long-term performance, safety, and reliability in electrical installations. Regular inspection and preventive measures can significantly extend the lifespan of the glands and the cables they protect. Here are some key maintenance and life extension methods:
- Regular Inspection: Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage, especially in harsh environments where moisture and chemicals may degrade the gland over time.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Dirt and debris can accumulate around the gland, affecting its sealing capability. Cleaning and applying a suitable lubricant (for metal cable glands) can prevent rust and ensure smooth operation.
- Proper Installation: Ensuring that the cable gland dimensions and cable gland diameters match the cables prevents strain and enhances sealing effectiveness. Incorrect installation can lead to premature failure.
- Replacement of Worn Components: Over time, sealing rings and gaskets in sealed cable glands may degrade. Replacing these components prevents leakage and maintains the enclosure's protection.
- Use of Corrosion-Resistant Materials: In marine or chemical industries, opting for stainless cable glands reduces the risk of corrosion and extends the gland’s service life.
Ensuring Proper Tightening: Over-tightening can damage the gland and cable, while under-tightening may lead to loose connections. Following manufacturer torque specifications is crucial.
- Simple and fast to install
- Excellent strain relief
- Effective environmental seal
Part No. Applicable Heaters Outer Jaket
PG-HS114 FBL/HSR 10/16 / 24w models Polyolefin -CP
all FBX / FBZ models Fluoropolymer -CT
PG-HS112 FBL/HSR 10/16 / 24w models Fluoropolymer -CF
PG-HS135 FBL / HSR 30w models Fluoropolymer -CF
PG-HS137 FBL / HSR 30w models Polyolefin -CP
PG-HS125 FBH 15/30 / 45w models Fluoropolymer -CT
PG-HS136 FBH 60w models Fluoropolymer -CT
 Türkçe
Türkçe